Photosynthesis
What is Photosynthesis?
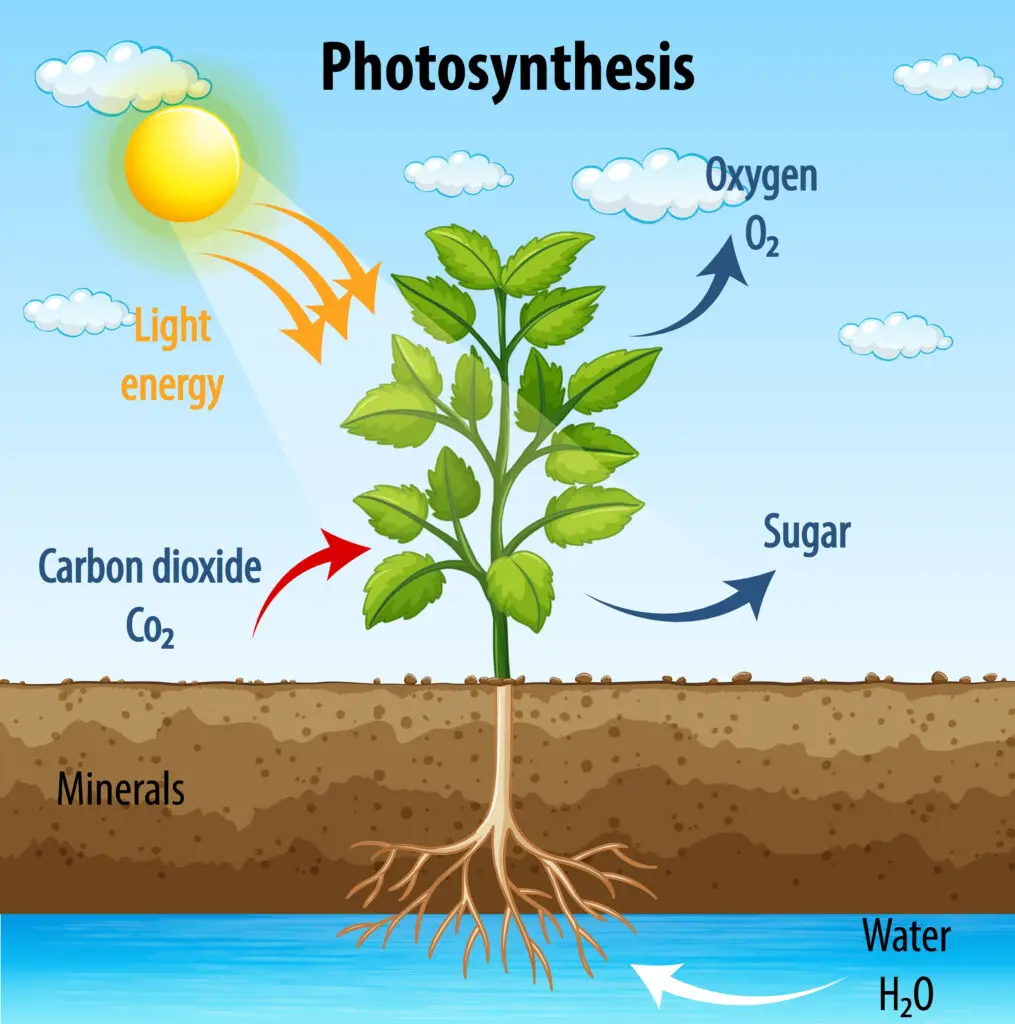
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce glucose and oxygen. Photosynthesis allows these organisms to create energy and is the primary source of energy for nearly all life on Earth.
How Plants Make Their Food
Photosynthesis is the process plants use to turn sunlight into food. It’s like a recipe where plants take sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide from the air and turn them into energy and oxygen. This process is what makes life on Earth possible!
How Photosynthesis Works
- Sunlight: Plants use sunlight as their energy source.
- Water: They take water from the soil through their roots.
- Carbon Dioxide: Plants absorb this gas from the air through tiny openings in their leaves.
- Chlorophyll: A green pigment in plants traps sunlight and starts the process.
The result? Plants make glucose, a type of sugar that gives them energy, and release oxygen into the air.
The Photosynthesis Equation
Here’s the simple formula:
Sunlight + Water + Carbon Dioxide → Glucose + Oxygen
Why Photosynthesis Is Important
- Creates Oxygen: Plants release oxygen, which humans and animals need to breathe.
- Provides Food: Plants use the glucose they make to grow, and other animals eat plants for energy.
- Cleans the Air: By taking in carbon dioxide, plants help reduce greenhouse gases.
Examples in Action
- Trees: Big trees like oaks and pines make oxygen for entire ecosystems.
- Grass: Helps feed animals like cows and rabbits.
- Aquatic Plants: Like algae, make oxygen underwater for fish and other marine life.
Challenges for Photosynthesis
- Lack of Sunlight: Plants can’t make food in the dark.
- Pollution: Harmful chemicals can block sunlight or damage plants.
- Deforestation: Cutting down forests reduces the number of plants doing photosynthesis.