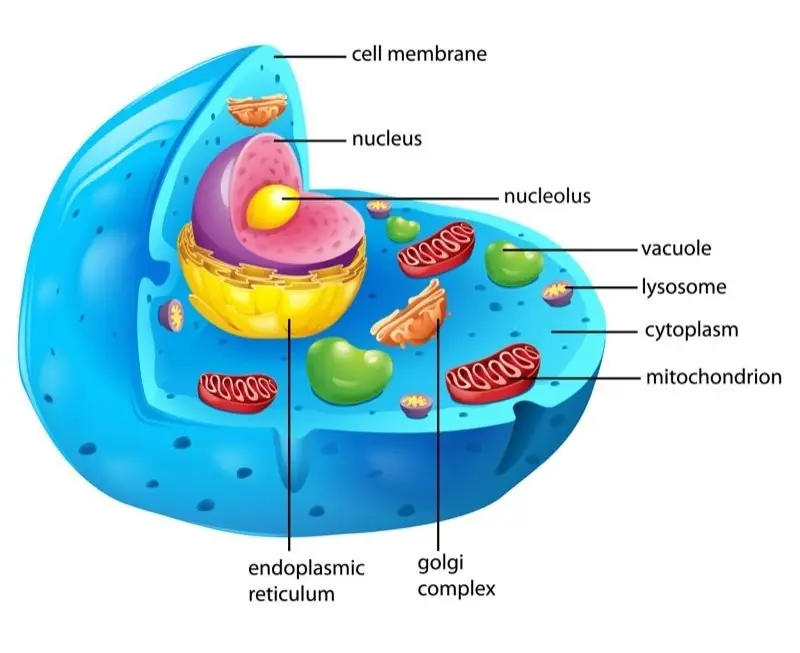
Cytoplasm
What is Cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm is the gel-like substance inside a cell that surrounds and supports organelles, allowing them to function and move within the cell. It provides a medium for chemical reactions and cellular processes.
Cytoplasm’s Role in the Cell
The cytoplasm is like a busy workspace inside a cell. It’s where all the action happens. It holds the organelles in place and provides the environment for chemical reactions. For example, enzymes in the cytoplasm break down nutrients to give the cell energy. It’s also a transportation area, helping materials move between organelles. Without cytoplasm, cells wouldn’t be able to function properly. It’s one of the key parts that keeps the cell alive and active.
How Cells Stay Organized
Cells can seem chaotic, but the cytoplasm keeps things under control. This jelly-like substance fills the cell and separates the organelles. It prevents them from bumping into each other and keeps their jobs organized. Cytoplasm also helps protect organelles from damage. Its consistency allows smooth movement while providing cushioning. Think of it like packing peanuts inside a box—it protects everything while allowing space to work.
Chemical Reactions in Cytoplasm
Many important processes take place in the cytoplasm. One key process is glycolysis, where sugar is broken down into energy. Other reactions, like protein synthesis, also happen here. These processes are crucial for the cell’s survival. The cytoplasm acts like a lab, providing the right environment for these reactions. It’s full of nutrients, enzymes, and other molecules that make these activities possible.
Transport Inside the Cell
Cytoplasm acts like a highway for the cell. Materials like proteins and nutrients travel through it to reach different organelles. For example, ribosomes floating in the cytoplasm build proteins, which are then moved to other parts of the cell. This movement ensures everything gets where it needs to go. The cytoplasm’s fluid nature makes transport quick and efficient, keeping the cell active and productive.