Deoxyribonucleic Acid
What is DNA?
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) is the molecule that contains the genetic information of an organism. It is found in the nucleus of cells and provides the instructions for building and maintaining the organism, passing traits from one generation to the next.
The Cell’s Blueprint
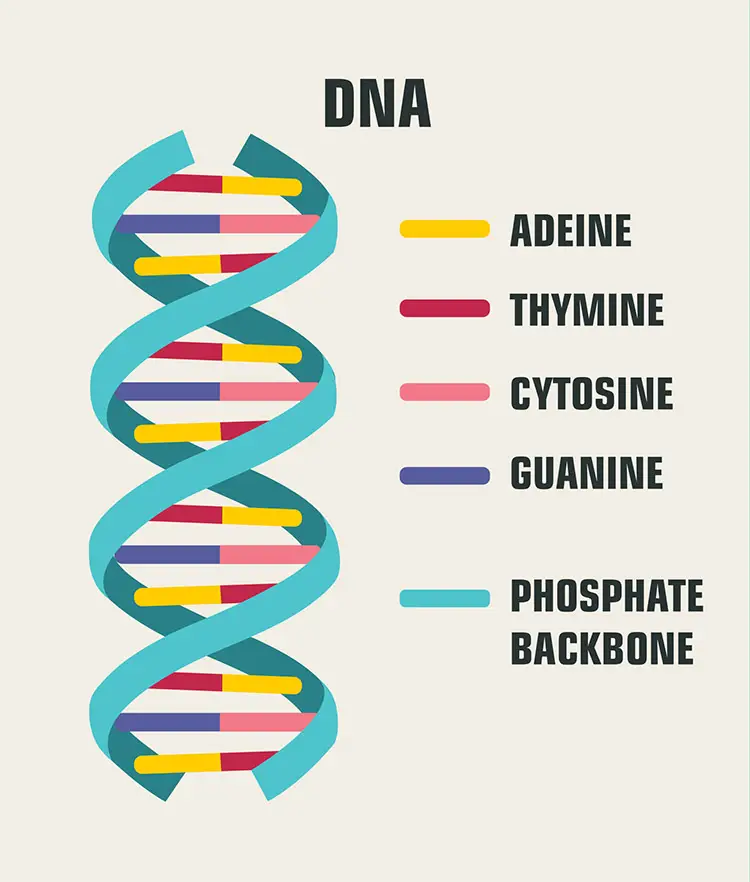
DNA serves as a blueprint for all living organisms, guiding the building and operation of the cell. It organizes its instructions in a code made of four chemical bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). The specific order of these bases creates genes, which determine traits such as eye color and height. Cells store DNA in the nucleus, packing it tightly into structures called chromosomes. Without DNA, cells lose the ability to grow, repair, or reproduce, making it essential for life.
How Traits Are Passed On
DNA is the reason you inherit traits from your parents. During reproduction, DNA from both parents combines to form a new set of instructions. This mix of DNA determines everything from your physical features to certain health risks. Scientists study how genes in DNA are passed down, a field known as genetics. Understanding DNA helps explain how families share similar traits, and why siblings can look alike but still be unique.
DNA in Everyday Life
DNA isn’t just important inside cells—it has practical uses too. Forensic scientists use DNA to solve crimes by matching samples to suspects. DNA tests can also help people learn about their ancestry. In medicine, doctors study DNA to understand genetic diseases and develop personalized treatments. These applications show how DNA impacts life far beyond the microscopic level, connecting biology with real-world solutions.
The Role of DNA in Protein Production
DNA provides the instructions cells need to make proteins, which are essential for life. During transcription, the cell copies the DNA code into RNA, ensuring the instructions are ready for the next step. The RNA then travels to a ribosome, where the cell translates the code into a protein. These proteins carry out countless tasks, such as repairing tissues and fighting infections, keeping the organism healthy and functioning. This entire process, beginning with DNA, drives how cells operate. Without DNA, the cell couldn’t produce proteins, making life as we know it impossible.