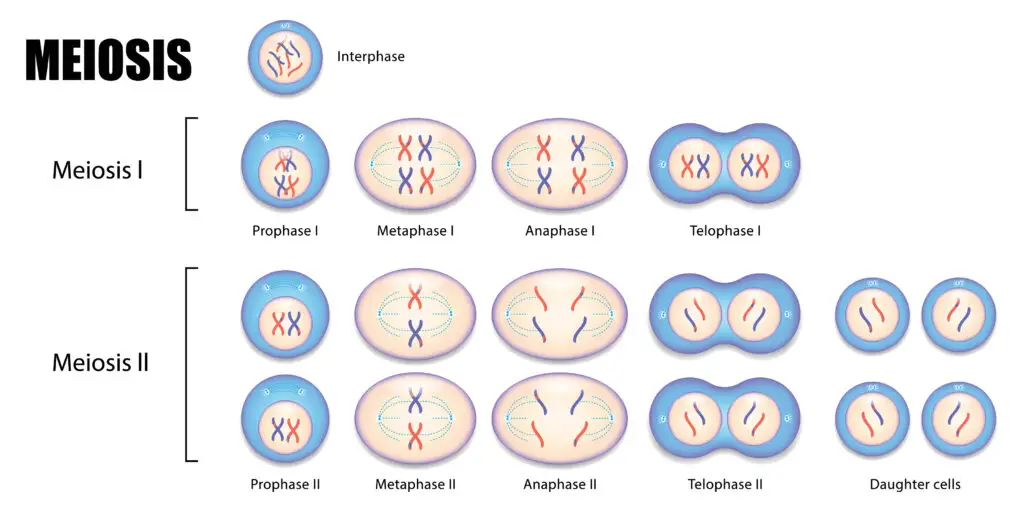
Meiosis
What is Meiosis?
Meiosis is a type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, creating four genetically unique daughter cells. Meiosis is crucial for sexual reproduction, as it produces gametes (sperm and egg cells) with half the genetic material of the parent cell.
Purpose & Stages
The purpose of meiosis is to create special cells called gametes (like sperm and egg cells) that are used for reproduction. These cells have half the usual number of chromosomes, so when they combine during fertilization, they create a new cell with the correct number of chromosomes.
Meiosis happens in two stages, called Meiosis I and Meiosis II. Each stage has several steps.
Meiosis I:
- Prophase I: The chromosomes pair up, and they exchange small pieces of DNA. This process, called crossing over, helps create genetic variety.
- Metaphase I: The chromosome pairs line up in the middle of the cell.
- Anaphase I: The pairs of chromosomes are pulled apart to opposite sides of the cell.
- Telophase I and Cytokinesis: The cell splits into two, with each new cell having half the number of chromosomes.
Meiosis II:
- Prophase II: The chromosomes in each of the two cells prepare to divide again.
- Metaphase II: The chromosomes line up in the middle of each cell.
- Anaphase II: The chromosomes are split into two halves, called chromatids, which are pulled to opposite sides of the cells.
- Telophase II and Cytokinesis: Both cells split again, creating four new cells. Each of these cells has half the number of chromosomes as the original cell.
Mitosis vs. Meiosis
Purpose:
- Mitosis happens when a cell needs to make an exact copy of itself. This is how your body grows and repairs itself. For example, if you get a cut, mitosis helps create new skin cells to heal the wound.
- Meiosis, on the other hand, is used to create reproductive cells like sperm and eggs. These cells have half the normal number of chromosomes, so when they combine during reproduction, the offspring gets the right amount of DNA.
Number of Divisions:
- Mitosis involves one division. The cell splits once to create two identical cells.
- Meiosis involves two divisions. It starts with one cell and ends with four cells, each with half the number of chromosomes.
Number of Chromosomes:
- In mitosis, the new cells have the same number of chromosomes as the original cell. If the original cell has 46 chromosomes, the new cells also have 46.
- In meiosis, the new cells have half the number of chromosomes. If the original cell has 46 chromosomes, the new cells have 23.
Genetic Differences:
- Mitosis creates cells that are identical to the original cell. This is important for growth and repair.
- Meiosis creates cells that are genetically different. This happens because of crossing over, which mixes up the DNA, leading to variety in offspring.
Summary:
Mitosis is for growth and repair, making identical cells. Meiosis is for reproduction, making unique cells with half the number of chromosomes. Both are important for keeping your body and future generations healthy!