Metaphase
What is Metaphase?
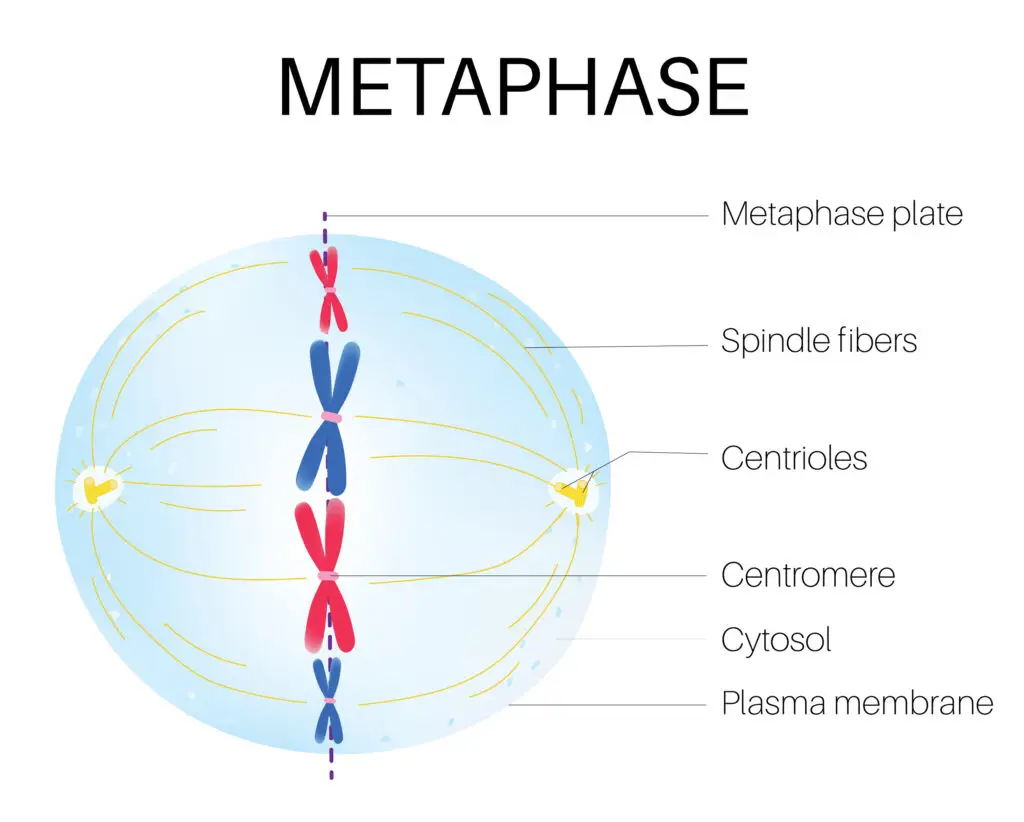
Metaphase is the stage of mitosis where chromosomes align in the center of the cell, along the metaphase plate. The alignment ensures that each new cell will receive an identical set of chromosomes.
Aligning Chromosomes
In metaphase, the second stage of mitosis, the chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell along an imaginary line called the metaphase plate. Spindle fibers attach to each chromosome at its centromere, making sure the chromosomes are ready to be pulled apart. This alignment ensures that both new cells will get an identical set of DNA. Metaphase works like an organizing step before the cell splits its genetic material.
What Happens During Metaphase
In metaphase, the chromosomes, now tightly packed, line up in the middle of the cell. Spindle fibers from opposite sides of the cell attach to each chromosome’s centromere, holding them in place. This setup ensures the chromosomes are evenly divided later. Proper alignment is crucial because mistakes could cause the new cells to get the wrong amount of DNA, which might lead to problems.
Importance in Biology
Metaphase ensures that genetic material is divided evenly between the two new cells. The precise alignment of chromosomes allows the spindle fibers to separate sister chromatids accurately in the next phase, anaphase. Without this careful organization, cells could end up with too many or too few chromosomes, leading to genetic disorders or cell death. Metaphase is critical for maintaining genetic stability.
The Role of Spindle Fibers
Spindle fibers play a key role in metaphase. They extend from centrioles at opposite poles and attach to chromosomes at their centromeres. These fibers exert tension, pulling the chromosomes into a straight line along the metaphase plate. This ensures that when the chromatids separate, they are pulled toward opposite ends of the cell with precision. The strength and accuracy of spindle fibers are vital for successful cell division.
Metaphase Checkpoint
During metaphase, the cell checks that everything is lined up correctly. It makes sure all chromosomes are attached to spindle fibers and positioned in the middle of the cell along the metaphase plate. If something isn’t right, the cell stops and fixes the problem before moving to anaphase. This checkpoint helps prevent mistakes in separating the chromosomes, keeping the cell safe from mutations or imbalances.
Metaphase in the Cell Cycle
Metaphase is a short but crucial stage in mitosis. It follows prophase, where chromosomes prepare for alignment, and precedes anaphase, where chromatids are separated. The successful completion of metaphase ensures the cell can divide its DNA evenly, leading to healthy daughter cells. Its precise mechanics make metaphase a key step in the overall cell cycle.