Mitochondrion
Definition of Mitochondrion
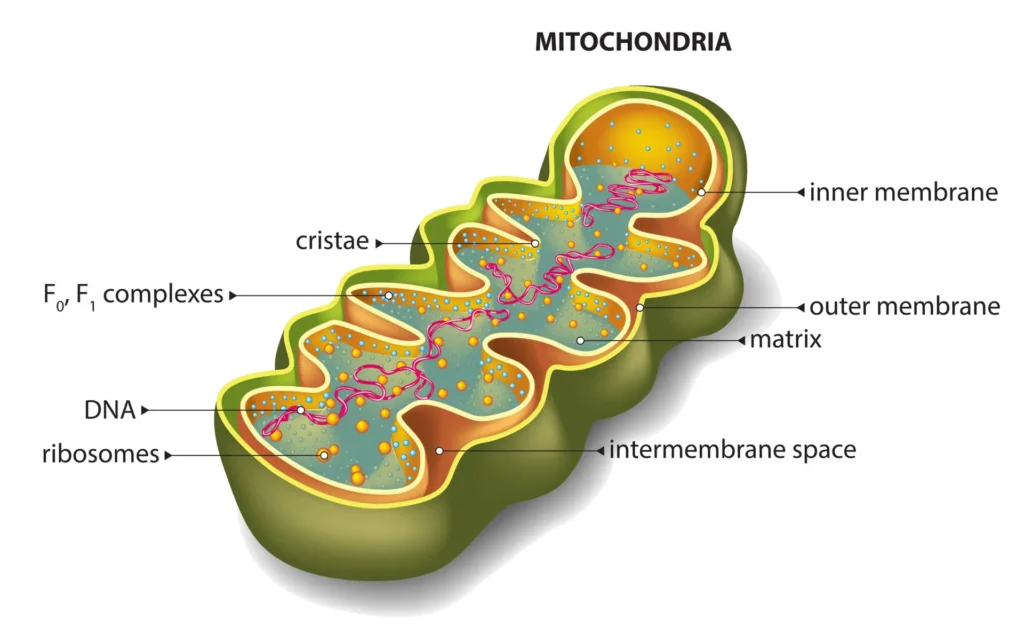
The mitochondrion is an organelle known as the “powerhouse” of the cell, as it produces energy by converting nutrients into ATP (adenosine triphosphate). This energy powers the cell’s activities and is essential for cellular functions.
Function and Energy Production
Mitochondria are like tiny power plants inside your cells. Their main job is to make energy that your body can use. Here’s how they do it in a way that’s simple to understand:
- Energy Source: Just like a car needs fuel, your cells need energy. Mitochondria make energy from the food you eat, especially sugars and fats.
- ATP – The Energy Packets: Mitochondria turn food into a special kind of energy called ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate). Think of ATP as tiny packets of energy that power different parts of your body, from your muscles to your brain.
- Process of Cellular Respiration: The mitochondria use a process called “cellular respiration” to make ATP. In this process, they take in oxygen (from the air you breathe) and combine it with food molecules, breaking them down and releasing energy.
- Oxygen In, Carbon Dioxide Out: Mitochondria use oxygen and produce carbon dioxide as a waste product, similar to how we breathe. This is why you need to breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide – it helps your mitochondria work!
- Why They’re Important: Without mitochondria, cells wouldn’t have the energy they need to move, grow, or even keep you alive. They’re essential for everything your body does.
In short, mitochondria are like tiny batteries in your cells, keeping them charged and active so you can do all the things you love!
Mitochondrial Diseases
Mitochondrial diseases occur when the mitochondria in cells don’t function as they should. Normally, mitochondria are responsible for making energy. However, when mitochondria don’t work properly, cells don’t get enough energy to function well. As a result, people with mitochondrial diseases can feel very tired and weak. Furthermore, this lack of energy can cause issues in different parts of the body, especially in muscles, the brain, and the heart. These organs are particularly affected because they need a lot of energy to work correctly.
Mitochondrial diseases can have different symptoms, such as muscle weakness, vision problems, or learning difficulties, and they can affect people differently. Although there’s no cure, doctors can help manage the symptoms with treatments like special diets or exercises. Many mitochondrial diseases are inherited, meaning they’re passed down from parents, and they affect how cells get the energy they need to keep the body running.