Organelle
What is an Organelle?
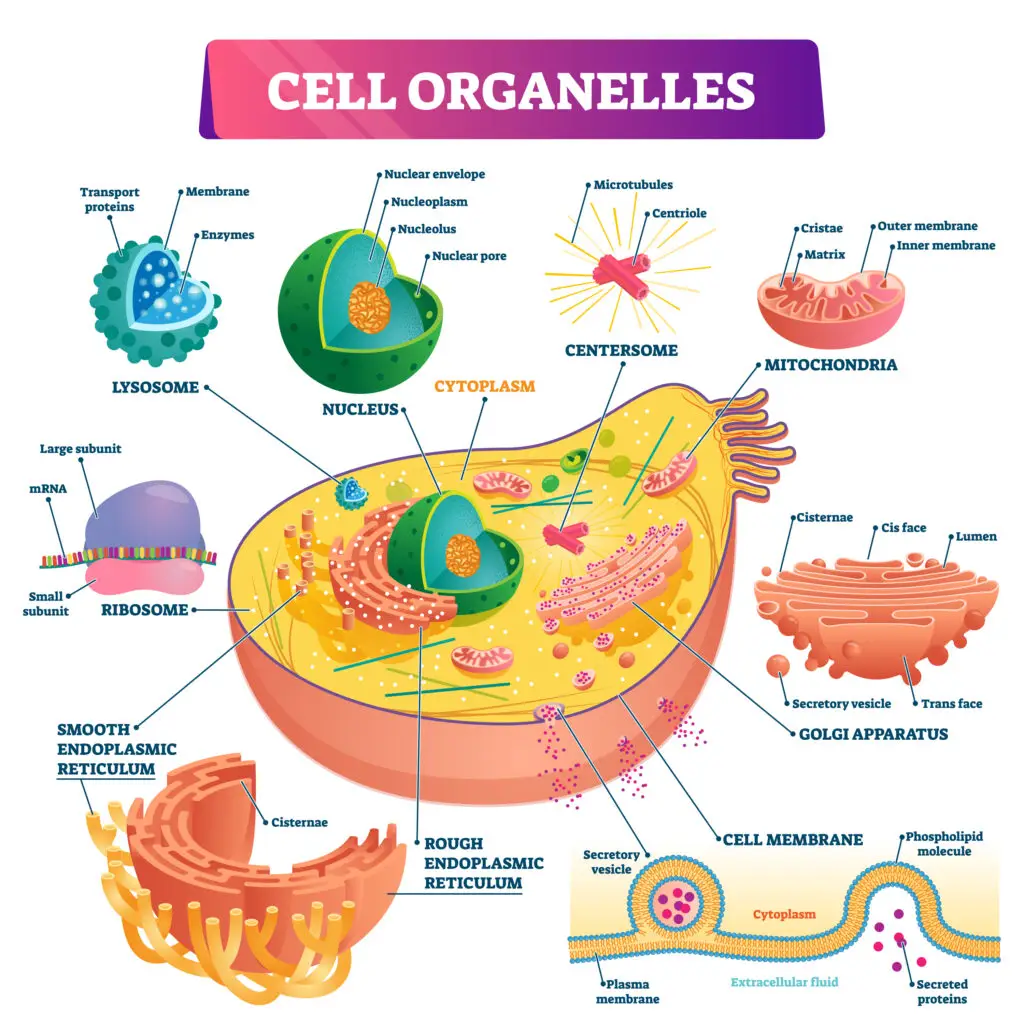
An organelle is a specialized structure within a cell that performs specific functions, much like organs in the body. Examples of organelles include the nucleus, mitochondria, and ribosomes, each with a unique role in cell function.
Organelle Functions in Cells
Organelles are like tiny machines inside a cell. Each one has a specific job to keep the cell alive and working. For example, the mitochondria provide energy, like a battery for the cell. The nucleus acts as the control center, giving instructions for the cell’s activities. Other organelles, like the ribosomes, help make proteins that the cell needs. All of these parts work together to keep the cell healthy and functioning, much like a factory with different departments.
How Cells Stay Organized
Cells are packed with organelles, each with its own job. To keep things running smoothly, organelles stay in specific areas within the cell. The cytoplasm, a jelly-like substance, holds everything in place. Membranes surround many organelles to separate their work from other cell processes. This organization helps the cell do many tasks at once without getting mixed up. It’s like a busy kitchen where everyone has their own station.
Organelle Roles in Plant Cells
Plant cells have some organelles that animal cells don’t. For example, chloroplasts capture sunlight to make food through photosynthesis. This gives plants the energy to grow and thrive. Plant cells also have a large central vacuole that stores water and nutrients. This vacuole helps plants stay upright by keeping the cells firm. These unique organelles highlight how plant cells specifically design themselves to meet their needs.
The Role of the Mitochondria
Mitochondria are often called the “powerhouses” of the cell. They turn food into energy that the cell can use. This process, called cellular respiration, happens inside the mitochondria. Cells with high energy needs, like muscle cells, have more mitochondria to meet the demand. Without mitochondria, cells wouldn’t have the energy to move, divide, or repair themselves. This makes them one of the most important organelles in both plant and animal cells.