Natural Selection
Natural selection is a key mechanism of evolution, first introduced by Charles Darwin in 1859. It explains how populations change over time as individuals with beneficial traits are more likely to survive and reproduce. These traits become more common, helping populations adapt to their environment. Along with mutation, genetic drift, and gene flow, natural selection shapes the diversity of life on Earth.
How Natural Selection Works
Natural selection operates on the variation that exists within a population. This variation arises from genetic mutations, which create differences in traits such as size, color, or behavior. The following four principles are essential for natural selection to occur:
- Variation in Traits:
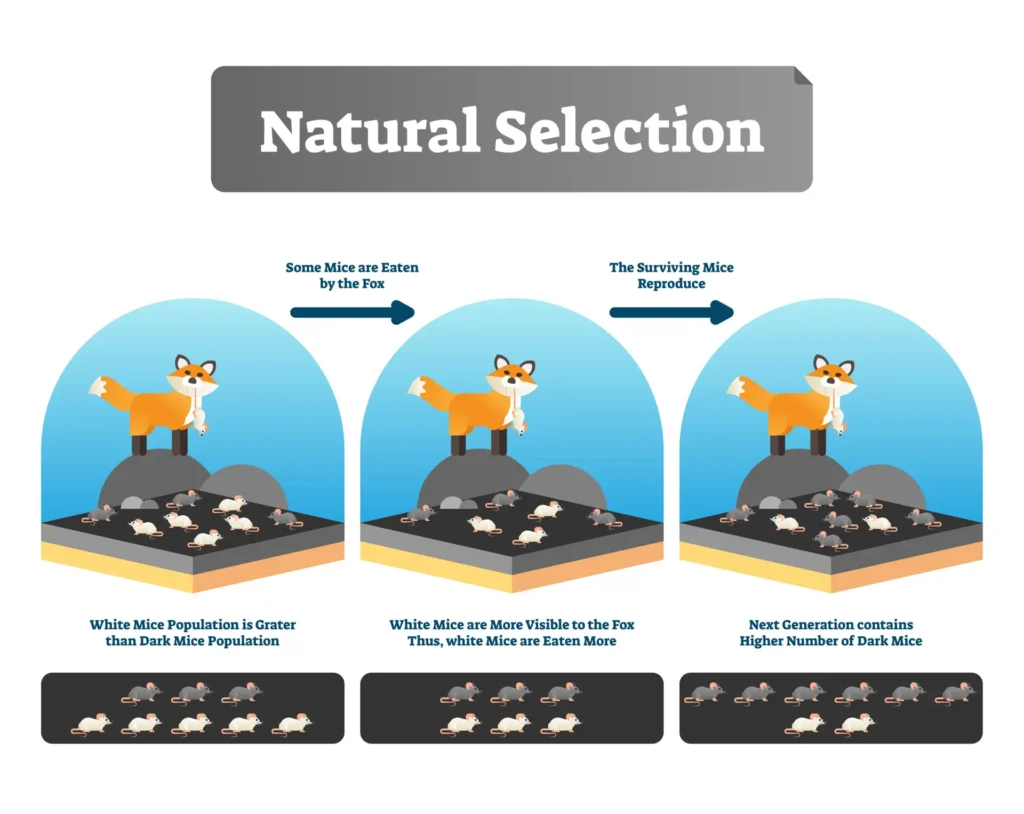
- Within any population, individuals exhibit variation in their traits. These traits may include physical characteristics like beak size or coloration, or behavioral traits such as mating calls or hunting strategies. This variation is primarily due to mutations and recombination of genes during reproduction.
- Differential Survival and Reproduction:
- In a given environment, some individuals are better suited to survive and reproduce than others. Those with advantageous traits have a higher chance of surviving long enough to reproduce and pass their genes on to the next generation. This is often referred to as “survival of the fittest.”
- Inheritance of Traits:
- The traits that contribute to an individual’s survival and reproduction are heritable. This means that the offspring of these individuals are more likely to inherit those beneficial traits, increasing the likelihood of their own survival and reproduction.
- Adaptation Over Time:
- Over many generations, the frequency of beneficial traits increases in the population. This leads to the gradual adaptation of the population to its environment. As a result, species become better suited to survive in specific environments or ecological niches.
Examples of Natural Selection
- Peppered Moths:
- A classic example of natural selection is the peppered moth (Biston betularia) in England. Before the Industrial Revolution, most peppered moths had light-colored wings, camouflaging them against lichen-covered trees. As industrial pollution darkened the trees with soot, darker-colored moths (melanic form) gained a survival advantage by blending in better. Over time, the population shifted toward more dark-colored moths. This demonstrates directional selection, where the environment favors one extreme variation of a trait.
- Darwin’s Finches:
- The Galápagos finches studied by Charles Darwin are a famous example of natural selection. Each species has a unique beak shape, adapted to the food on its island. Finches with larger, stronger beaks crack open hard seeds, while those with slender beaks catch insects. During droughts, finches with beak shapes suited for the available food are more likely to survive and reproduce.
Types of Natural Selection
Natural selection can act in different ways, leading to various patterns of evolution within populations:
- Directional Selection:
This occurs when one extreme of a trait becomes favored, causing the population to shift toward that trait. For example, horse species grew larger over time because larger individuals were better suited for survival in open grasslands.
- Stabilizing Selection:
- In stabilizing selection, traits in the population stabilize around an average, and extreme variations are removed. For example, in human birth weight, infants with very low or very high weights face higher mortality rates, while those with average weights have a better chance of survival.
- Disruptive Selection:
- Disruptive selection occurs when both extremes of a trait are favored over the average. This can lead to the population splitting into two distinct groups. For example, in certain species of birds, individuals with either very large or very small beaks are more successful in obtaining food, while those with medium-sized beaks are at a disadvantage.
Importance in Evolution
Natural selection is the primary mechanism by which populations adapt to their environments. It plays a central role in the theory of evolution by explaining how species evolve over time in response to environmental changes. This process leads to the development of new traits, species, and biodiversity. Over long periods, natural selection can result in speciation, the formation of new species, as populations diverge and adapt to different ecological niches.
Additionally, natural selection contributes to coevolution, where two or more species influence each other’s evolution. For example, predator-prey relationships often lead to adaptations in both species—predators may evolve sharper claws or faster speeds, while prey species may develop better camouflage or defensive mechanisms.
Human Impact
Human activities have increasingly influenced natural selection, both positively and negatively. Artificial selection is a human-driven process where individuals with desirable traits are selectively bred. This is common in agriculture and animal breeding, shaping crops, livestock, and pets.
In contrast, human-induced changes like pollution, habitat destruction, and climate change have intensified evolutionary pressures. For example, the use of antibiotics has caused the rapid evolution of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, a major public health issue.ncern.