Photosynthesis
/tab
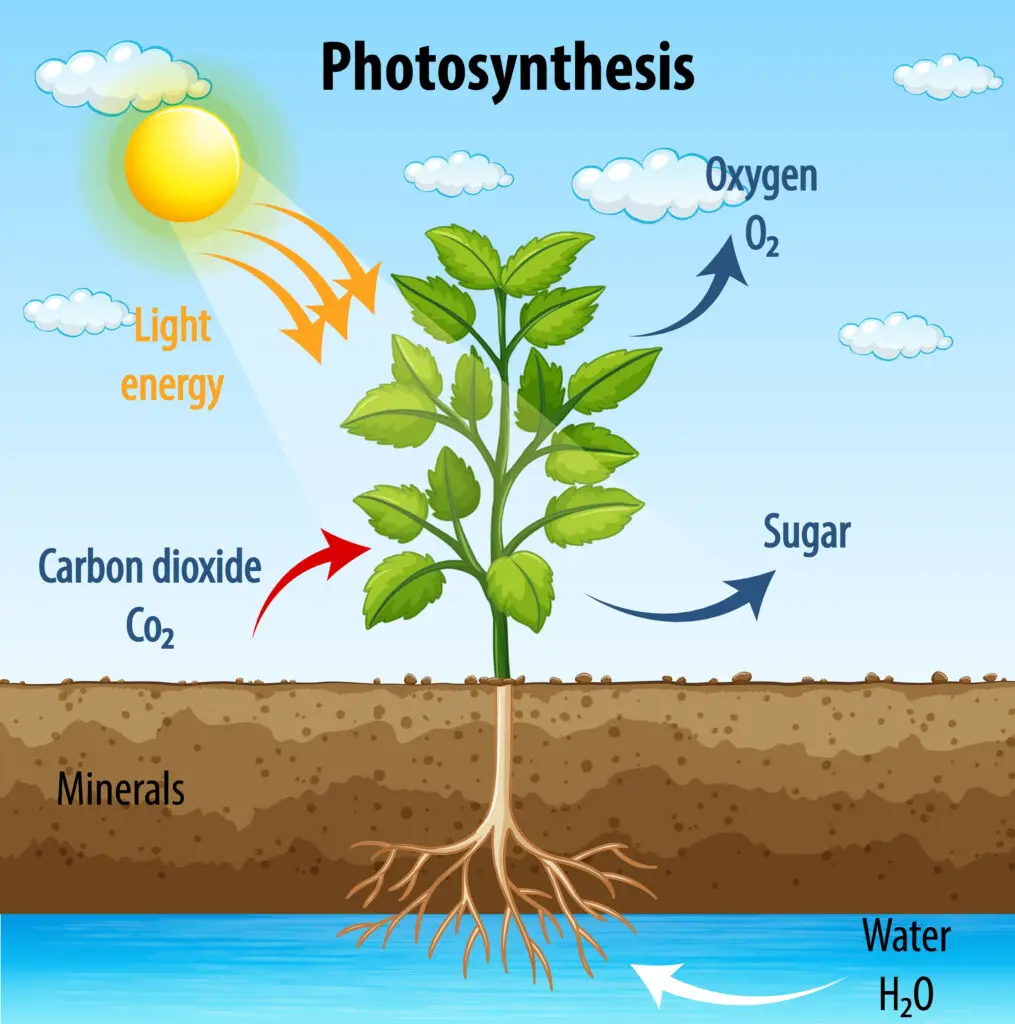
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy in the form of glucose (a type of sugar). This process not only provides the energy that plants need to grow and thrive but also produces oxygen, a byproduct essential for life on Earth. Photosynthesis is the foundation of the food chain and sustains almost all life by producing the energy that fuels ecosystems. Understanding how this process works helps us appreciate the critical role it plays in maintaining the planet’s balance.
The Basics of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis takes place primarily in the chloroplasts of plant cells, which contain a green pigment called chlorophyll. Chlorophyll captures sunlight, allowing plants to transform carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the air and water (H₂O) from the soil into glucose and oxygen.
Stages
Photosynthesis occurs in two major stages: the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle (also known as the light-independent reactions or the dark reactions).
1. Light-Dependent Reactions
The light-dependent reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts and require sunlight to proceed. These reactions capture light energy and convert it into chemical energy as ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate), which the plant uses in the next stage of photosynthesis.
- Chlorophyll absorbs light energy, which excites electrons and triggers a series of reactions.
- Photolysis splits water molecules (H₂O), releasing oxygen (O₂) as a byproduct and providing electrons and protons for the energy-carrying molecules.
- The reactions produce energy, which is stored in ATP and NADPH and later used to synthesize glucose in the Calvin cycle.
2. Calvin Cycle (Light-Independent Reactions)
The Calvin cycle takes place in the stroma of the chloroplast and does not require light. Instead, it uses the ATP and NADPH generated in the light-dependent reactions to convert carbon dioxide (CO₂) into glucose.
- Carbon fixation: CO₂ is captured from the atmosphere and attached to a five-carbon sugar called ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP).
- Reduction: ATP and NADPH are used to reduce the carbon molecules into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P), a three-carbon sugar.
- Regeneration: Some G3P molecules leave the cycle to form glucose, while others are recycled to regenerate RuBP, allowing the cycle to continue.
This process allows plants to store energy as glucose, which they later use for growth, reproduction, and other vital functions. This glucose serves as the primary source of energy for the plant itself and for organisms that consume plants, making photosynthesis the basis of life on Earth.
The Importance of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is vital to life on Earth for several reasons:
- Oxygen Production:
- Photosynthesis is responsible for producing most of the oxygen in Earth’s atmosphere. The oxygen released as a byproduct of splitting water molecules during the light-dependent reactions is essential for the survival of aerobic organisms, including humans and animals.
- Energy for Life:
- Photosynthesis is the foundation of the food chain. Plants create glucose through this process, which herbivores consume, and in turn, carnivores consume those herbivores. Without photosynthesis, there would be no primary producers to provide energy for other organisms.
- Carbon Dioxide Reduction:
- Photosynthesis plays a crucial role in reducing carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere, helping to mitigate climate change. Plants act as a carbon sink, absorbing CO₂ during the Calvin cycle and storing it as glucose, thereby removing it from the atmosphere.
- Fueling Ecosystems:
- In ecosystems, photosynthesis supports a wide range of organisms, from small algae in aquatic environments to towering trees in forests. All living organisms, directly or indirectly, depend on the glucose produced through photosynthesis for energy.
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
Several factors influence the rate of photosynthesis in plants, including light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, temperature, and water availability.
- Light Intensity:
- Light is a key driver of photosynthesis, and the rate increases with increasing light intensity up to a certain point. However, if the light is too intense, it can damage the chloroplasts, reducing the plant’s ability to photosynthesize.
- Carbon Dioxide Levels:
- As CO₂ is a substrate for photosynthesis, higher concentrations of CO₂ can increase the rate of the process, up to the point where other factors become limiting.
- Temperature:
- Photosynthesis is an enzyme-driven process, so temperature affects its rate. Too low a temperature slows down the enzymatic reactions, while too high a temperature can denature the enzymes, inhibiting photosynthesis.
- Water Availability:
- Water is required for the light-dependent reactions, so a lack of water can limit the plant’s ability to photosynthesize. Drought conditions can reduce the rate of photosynthesis and limit plant growth.
Role in Human Life
Humans benefit immensely from photosynthesis, both directly and indirectly. The oxygen we breathe is produced by plants and algae through photosynthesis, and the food we consume is part of the energy cycle that begins with plants capturing sunlight.
- Agriculture:
- Photosynthesis is the backbone of agriculture. Crops such as wheat, rice, corn, and fruits rely on photosynthesis to grow and produce food for the world’s population. Improving our understanding of photosynthesis has led to advancements in agricultural productivity and food security.
- Fossil Fuels:
- Ancient plants and microorganisms captured sunlight through photosynthesis millions of years ago, forming the fossil fuels we use today, such as coal and oil. These fuels store energy originally derived from the sun, which is released when burned.
- Medicinal and Industrial Uses:
- Many of the medicinal compounds and industrial products used today come from plants, which rely on photosynthesis to grow. Natural compounds derived from photosynthetic plants are used in drugs, cosmetics, and other commercial applications.